Medical Science Study Program, Faculty of Medicine, Trisakti University
The Medical Science Study Program is an S1 stage of academic education that is equivalent to Indonesian National Qualifications Framework level 6. Graduates of the Medical Science Study Program have the right to bear the title of Medical Scientist. The curriculum used in the Medical Science Study Program is the Curriculum of Higher Education that is directed to the Indonesian Medical Competency Standards, the National Standards for Higher Education and the Indonesian National Qualifications Framework level 6 and aims to produce Medical Scientists of exemplary behavior, who are able to master medical science concepts, research, and basic clinical skills as foundation for further education, and to self-evaluate and self-develop by benefiting from science, technology and the arts.
The Curriculum of Higher Education is implemented with emphasis on Student-Centered Learning (SCL) through “cooperative” learning, the ”Collaborative Learning System” and ”Problem Based Learning” that direct the students to do more active learning. SCL aims to prepare graduates that are able to apply the principle of life-long learning by acquiring skills that can be used for self-guidance (independent learning).
The Curriculum of Higher Education of the Faculty of Medicine of Trisakti University is managed by using the SPICES learning strategy (Student-centered, Problem-based learning (PBL), Integrated Community-based learning, Elective or Early clinical exposure, and Systematic learning). The curriculum is planned in such a manner that hopefully the learning will be student-centered. The students are viewed as adult human beings such that they should be involved in determining their own learning goals. The task of the lecturers or educators is to facilitate the learning process. The process of determining the self-learning goals is trained mainly in the tutorial discussion process. The students are triggered by a clinical case (early clinical exposure) and are asked to determine the nature of the encountered problem and to decide what is to be learned. This type of learning corresponds to PBL. The curricular plan is made by integration, therefore it is not only based on one scientific field, but each problem is considered comprehensively from the standpoint of several scientific fields (integrated learning). The complexity of the problems with which the students are confronted is made to increase stepwise and is not interrupted from one stage to the next, such that a learning spiral is formed. The students are trained from the most basic up to the most complex stage (systematic learning). Based on an awareness of the gap between theory and field practice, the curriculum of the Faculty of Medicine of Trisakti University has been planned to bridge this gap by exposing the students to the community (community-based learning).
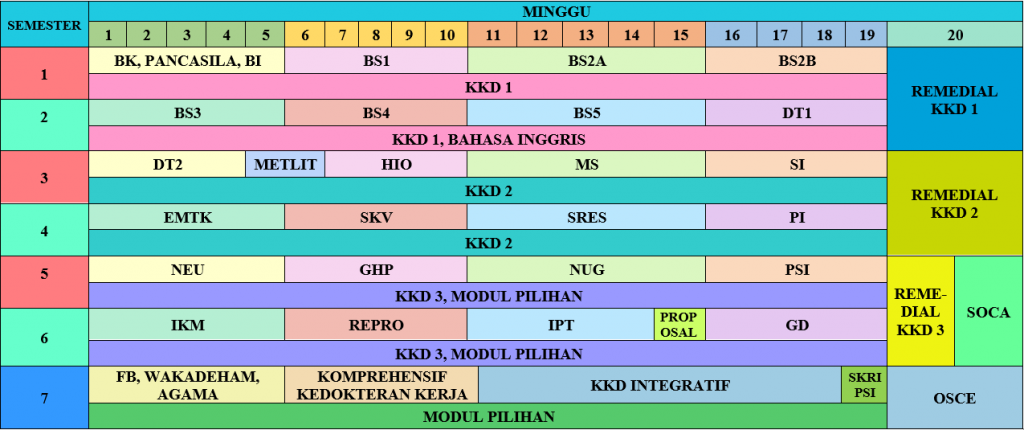
The curricular material of the Medical Science Study Program is presented in units called modules, which are produced by the integration of biomedical sciences*, basic clinical science*, clinical science*, community medicine* and supporting sciences* and are given in stages during seven semesters. Each module has a predetermined credit hours load such that overall the students are said to have graduated as Medical Scientist (Sked) after having completed 150 credit hours.
The learning process in each module is conducted in various ways to accommodate the students’ needs, comprising face-to-face activities (interactive lectures), tutorial group discussions, plenary sessions, practical work, and training of basic clinical skills.
Face-to-face activities
The face-to-face activities that are performed aim at assisting the students to understand the learning concept that associates the course content with the daily real-life situation and motivates the students to forge a link between knowledge and its application in daily life.